Browse the solutions provided by AIOTI members below.
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
AISTOR
AISTOR_SolarEdge_testbed |

Location: BEIA headquarters, Street Peroni 14, Disctrict 4, Bucharest, Romania |
(Renewable) Energy, Smart grid | Installing solar panels at a user's own home and connecting them to inverters with the purpose of becoming a prosumer, then being able to visualise in real time the power generation capabilities of each solar panel, so the user can determine their efficiency and ask for maintenance from the PV cell provider, in case of faulty functionality. Additionally, Solar Edge operators will have access to a dashboard of each user's PV cell "garden" and see their phyisical locations mapped geographically, along with their orientation and energy generation capabilities. Warnings and alerts can be generated by specifying certain parameters (the power generation falls under a certain threshold). |
License: Open
Access: local(operators can come and provide installation, maintenance) and remote (through the dashboard), based on agreement Contact: george@beia.ro, cristian.beceanu@beia.ro, robert.florescu@beia.ro, |
deployed testbed |
| Description: We are already seeing the large scale implementation of Photovoltaic cell implementation in suburban areas where single-family housing is the norm. A unified way of visualising the energy production in real time is an ideal step forward. The application can provide a histogram of energy generation, so the users can determine which PV cells are more efficient and what during which months there will be no need to draw energy from the electric grid | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: | Technology: MQTT, IoT, Renewable Energy, Energy Efficiency, InfluxDB | ||||
| Hardware Photovoltaic (PV) Cells, inverters | Software Grafana, Solar Edge, Java, API | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
L-GRECO
B5G/6G L-GRECO Athens platform |

Location: Athens, Greece |
Smart Connectivity | Mobility, Dual-connectivity, AI-assisted networking, User-centric networking, Edge-Cloud continuum |
License: n.a
Access: Local and remote upon request and on specific agreement Contact: koumaras@iit.demokritos.gr Dr. Harilaos Koumaras, NCSR Demokritos |
Deployed testbed |
| Description: B5G/6G L-GRECO platform [Athens, Greece], is a state-of-the-art large-scale testbed supporting 5G SA and B5G networks, cloud and edge infrastructures, IoT systems and AI applications. Located in Athens, the testbed expands across the campuses of NCSR Demokritos and OTE Academy that are interconnected through a dedicated 10G dark fiber, and hosts multiple physical and virtualized resources capable to support various simultaneous demands. It integrates orchestrators capable to support ad-hoc instantiation of tailored trial networks and automated life-cycle management and execution of large-scale experiments on top of these networks. Both enterprise-grade and open/experimental 5G cores are operated, with an assortment of mid-band and high-band radio access networks including satellite backhauling capabilities, thus offering the opportunity to study complex cases. A satellite/NTN emulator, is also integrated and enables low-cost, agile multi-operator and multi-access situations. The combination of all above components introduces multi-connectivity scenarios, to study how traffic is handled across different network connections, as well as over different administrative domains of the IoT-Edge-Cloud continuum. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: The concept is to provide a platform combining physical and virtual resources which can be orchestrated as a whole and be exposed to an experimentation methodology which by defining trial networks topologies can support the execution of a variety of user defined test cases. The details of each test case define the exact scenarios and network slices, which are deployed for the acquisition of a certain set of KPIs and KVIs which are used to evaluate networks behavior and equipment efficiency. | Technology: B5G, 6G, IoT, AI/ML, LoRAWAN | ||||
| Hardware B5G Cores:ATHONET 5G SA Core, Amarisoft 5G SA Core, RAN:ERICSSON Baseband Unit (BBU), ERICSSON Remote Radio Unit (RRU)/RAN, Indoor Radio Unit (IRU) 8848 and Dot 4479 B78L, Amarisoft 5G NR RAN, 5G enabled Raspberry PIs with sensors integrated, end user devices (5G smartphones), 5G-enabled vehicles (small scale), Nokia Airscale RAN, Plethora of IoT sensors. | Software OpenNEF, ETSI OpenCAPIF, OpenStack, OpenNebula, Proxmox, K8s, Amarisoft, Open5gs, OpenTAP, Fiware Orion NGSI-LD, open5genesis, 6G-SANDBOX TNLCM (trial network lifecycle manager), OpenMANO, MQTT, HomeAssistant IoT system, Network Monitoring & Measurement tools, COSMOTools | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
FarmSustainaBL
Enabling Smart Livestock Farming Technologies for Environmental Sustainability using Blockchain |

Location: Bucharest, Romania |
Agriculture | Farms |
License: open
Access: remote Contact: George Suciu, george@beia.eu |
proof of concept |
| Description: The main objective of the project is to apply a holistic approach for decreasing the GHG emissions derived from intensive livestock farming by optimizing the livestock production. For doing this, the consortium will monitor the animal feed, the animal behaviour and characteristics and the stable environment. Specifically, IoT devices will be installed in the farm for monitoring key parameters of the stable environment (temperature, humidity, gas sensors (NOx, COx, CH4, NH3, etc.), the animal (accelerometer, motion sensor, weight sensor, etc.) and the feed (flow sensor, weight sensor, humidity sensor etc.). | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: | Technology: | ||||
| Hardware | Software | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
F5G OpenLab
Enable twin transition – green and digital, through ubiquitous fiber connectivity. |
Location: Berlin, Germany |
Manufacturing, Health, Information and Communications Technology (ICT) | Cloud-based machine vision, cloud-based control of AGVs and robots, F5G use cases |
License: n.a.
Access: local and remote access possible, please contact us! Contact: contact@F5G-OpenLab.org Prof. Dr. Ronald Freund |
deployed testbed |
| Description: The F5G OpenLab is a novel testing and experimentation facility. Its objective is to make information and communication technologies (ICT) more sustainable by promoting optical-fiber-based Fifth Generation Fixed Networks (F5G). The F5G OpenLab is located at Fraunhofer HHI in Berlin. It was created to advance the validation of technologies and solutions that were defined by the Industry Specification Group (ISG) F5G of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). F5G OpenLab aims at gathering ICT demands and promoting fiber-to-the-X technologies, solutions and standards for application in vertical industries. The F5G OpenLab is open for members from vertical industries who want to implement a digital and green business model. It provides access to the latest innovations in fiber networks. Members get the chance to access blueprint designs for networks and leverage the benefits of fiber technology for all segments. The project’s testing lab evaluates novel components, systems and network designs. It offers a vendor-neutral experimental environment and a co-working space for validating new optical and mobile network solutions with respect to their bandwidth, latency and cloud requirements. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: Urban-area manufacturing site to edge cloud networking testbed with fully networked factory shop floor. | Technology: PON, OTN, WDM, WiFi,... | ||||
| Hardware PON/WiFi networks, edge cloud, robots, AGVs, vision inspection station, 3D printer, surveillance cameras, traffic generators, ... | Software network management systems, real-time telemetry and machine learning pipeline, distributed learning framework (DLFi) | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
PIMEO AI
PIMEO AI Testbed |

Location: Bucharest, Romania |
Water quality | complete suites of water quality measurements in all types of sensitive aquatic ecosystems |
License: open
Access: remote Contact: george@beia.eu - George Suciu |
proof-of-concept |
| Description: PIMEO AI targets the development and operational use in multiple representative environments of an artificial intelligence (AI) powered unmanned surface vehicle (USV) that is capable to perform complete suites of water quality measurements in all types of sensitive aquatic ecosystems. The resulting PIMEO AI USV will be a next-generation advanced analysis tool for studying sensitive ecosystems, identifying pollution sources, and mapping their environmental impact. It will fill an important market need for comprehensive water quality USVs, the market today being highly limited and aimed primarily at hydrology research. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: key technological blocks supported | Technology: IoT sensors, energy efficient sensors | ||||
| Hardware data loggers, iot sensors, Gateways | Software data connectors - REST and MQTT based, timeseries database, open source data visualziation tool | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
SAFECARE
|

Location: Romania |
Energy | use-cases supported |
License: type of licensing, for instance, open, MIT, Eclipse. If there are IPRs, please state so.
Access: local and remote, based on a specific agreement, etc. Contact: robert.kecs@beia.ro; robikecs1234@gmail.com; robert.florescu@beia.ro |
deployed testbed |
| Description: The aim of SAFECARE is to provide solutions that will improve physical and cyber security in a seamless and cost effective way. Thereby, it promotes new technologies and novel approaches to enhance threat prevention, threat detection, incident response and mitigation of impacts. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: | Technology: MQTT, IoT,BTMS | ||||
| Hardware Data loggers, IoT, | Software MQTT, JS, Python, C/C++, blockchain, surveilance | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
SEALEDGRID
Testing and Evaluating Sophisticated information and communication Technologies for enaBling scalablE smart griD Deployment |

Location: Romania |
Energy | use-cases supported |
License: type of licensing, for instance, open, MIT, Eclipse. If there are IPRs, please state so.
Access: local and remote, based on a specific agreement, etc. Contact: robert.kecs@beia.ro; robikecs1234@gmail.com; robert.florescu@beia.ro |
deployed testbed |
| Description: The rapid evolution of ICT has revealed the potential for centrally monitoring, controlling, and optimising the power grid. In this context, a more intelligent, responsive, and efficient, system has been devised, known as the Smart Grid (SG). As explained in the EU Third Energy Package the SG will support a dynamic two-way information exchange between utility companies and their customers, contributing towards a smart and sustainable energy management in Europe and the establishment of a wiser energy consumption mentality. However, besides the benefits of such an endeavour, the power grid will be exposed to security threats inherited from the ICT sector, while privacy issues and new vulnerabilities, related to the specific characteristics of the SG infrastructure, will emerge. The problem is assessed as crucial, if we consider that a potential attack to the SG may lead to cascading failures, ranging from destruction of other interconnected critical infrastructures to loss of human lives. Thus, the development of a security platform tailored to the SG is required, that i) can efficiently manage the plethora of SG nodes, ii) deal with potential malicious hardware or software modifications due to the physical access of the customers to the SG nodes, and iii) operate over heterogeneous systems. Considering all the above, SealedGRID aims at bringing together experts from industry and academia from cross-sectorial research areas having complementary background with the long-term goal to design, analyse, and implement a scalable, highly trusted and interoperable SG security platform. The platform will combine, for the very first time, technologies like Blockchain, Distributed Hash Tables, Trusted Execution Environments, and OpenID Connect, while for its realization the SealedGRID consortium is committed to a fully-integrated and multi-disciplinary secondment programme combined with a set of networking, dissemination, and exploitation activities. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: | Technology: MQTT, IoT, | ||||
| Hardware Data loggers, IoT, Solar Panels, Inverters, | Software MQTT, JS, Python, C/C++, blockchain | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
SS-IoT
SmartSantander IoT Testbed |

Location: Santander, Spain |
Smart cities, Cross-domain | Smart Parking, waste management, water management, street lighting |
License: not available
Access: local based on a specific agreement Contact: luis@tlmat.unican.es, Luis Muñoz |
deployed testbed |
| Description: SmartSantander proposes a unique in the world city-scale experimental research facility in support of typical applications and services for a smart city. This unique experimental facility will be sufficiently large, open and flexible to enable horizontal and vertical federation with other experimental facilities and stimulates development of new applications by users of various types including experimental advanced research on IoT technologies and realistic assessment of users’ acceptability tests. | |||||
|
|||||
| Concept: SmartSantander-IoT is aiming at fostering the digital transformation of the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors leveraging on the experiences and success of the Internet of Things initiatives in which University of Cantabria and Santander Municipality have been leading in the past. As such, this testbed aims at offering technical support and guidance as well access to a plethora of enablers, tools, APIs, and data for implementing and assessing concrete solutions fitting the corresponding requirements. | Technology: IoT, LoRaWan, WSN, Digital twin, Open Data, Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning | ||||
| Hardware On-Premises, Edge and Cloud combined. Gateways and nodes LoRaWan, IoT IP-enabled devices, e.g., sensors, Raspberry Pis with sensors, Beaglebones, etc. end-user devices, e.g., smartphones, tablets, laptops; cameras. | Software Based-on FIWARE components for the development of intelligent solutions and services. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
TESTBED2
Testing and Evaluating Sophisticated information and communication Technologies for enaBling scalablE smart griD Deployment |

Location: International:, USA, Nebraska, Princeton, California; Greece, Marousi; UK, Durham, Newcastle, Edinburgh; France, Paris; Germany, Tuebingen; Austria, Klagenfurt; Netherlands, Haarlem; Romania, Bucharest; Switzerland, Poidoux; China, Beijing, Nanjing, Guangzhou |
Energy, Computational Efficiency, Smart Grid |
License:
Access: local and remote, based on a specific agreement. Contact: robert.florescu@beia.ro |
deployed testbed | |
| Description: The increased computational complexity of decision making in extensive smart grid networks and limited performance due to unoptimized large-scale implementations of smart grids have lead to an urgent call-to-action. Thanks to the MQTT protocol, the ability of accessing IoT sensor data remotely has made maintenance and repairing tasks an ease, as there is no longer a necessity to waste specialists time on localizing the source of the issue. Additionally, IoT has offered consumers live access to their consumption data, thus facilitating the payment of bills. Blockchain together with cryptography has made significant improvements to the underlying security of the network, by firstly ensuring the authenticity of the information circulated between network nodes and secondly by scrambling the data, in order to prevent potential malicious users from finding out essential information regarding the consumer’s energy usage habits. Artificial Intelligence aims at optimizing the information flow and integrating supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) into the network, thus providing interoperability with existing grid architecture. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: key technological blocks supported | Technology: MQTT, IoT, Blockchain | ||||
| Hardware Smart Meters, Inverters, Photvoltaic cells, Electrical grid infrastructure, FIDO | Software XACML, AuthZ, FIDO, Keycloak | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
VITAL5G
Testing and Evaluating Sophisticated information and communication Technologies for enaBling scalablE smart griD Deployment |

Location: Galati, Romania |
Transport | use-cases supported |
License: type of licensing, for instance, open, MIT, Eclipse. If there are IPRs, please state so.
Access: local and remote, based on a specific agreement, etc. Contact: robert.kecs@beia.ro; robikecs1234@gmail.com; robert.florescu@beia.ro |
deployed testbed |
| Description: The VITAL-5G project plans to showcase the added-value of 5G connectivity for the European T&L sector by adopting a multi-modal approach containing major logistics hubs for freight and passengers (sea ports, river ports, etc.) | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: | Technology: MQTT, IoT, 5G | ||||
| Hardware Data loggers, 5G tranceivers, Video, AIS. | Software MQTT, JS, Python, C/C++ | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
Aalto
Aalto University Factory of the Future |
Location: Helsinki, Finland |
Manifacturing, energy, agriculture, mobility, logistics | Predictive maintenance, human robot interaction, collaborative robots, flexible production, Low electric vehicles. |
License: https://version.aalto.fi/gitlab/afof
Access: partner access feasible Contact: Dr Udayanto Dwi Atmojo udayanto.atmojo@aalto.fi, Prof. Valeriy Vyatkin valeriy.vyatkin@aalto.fi |
Testbed |
| Description: The Aalto Factory of the Future 1 is a facility for innovation and education of future industrial automation, industry 4.0 and beyond. It is a space shared by humans, robots, and production stations, which serves as a platform for projects in advanced information technologies applied to future production systems. It focuses on achieving revolutionary high flexibility by exploiting the architecture of modular autonomous intelligent production units. We have access to enabling technologies for production systems that include AI, IIoT, wireless (5G, Wi-Fi 6, LoraWAN) connected to Aalto 5G Test Network, edge/fog/cloud computing paradigms, VR/AR. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: Distributed automation system in hyper flexible production system based on modular production units | Technology: IT/OT integration ranging from IEC 61131-3, IEC 61499, OPC UA, 5G, WiFi6, TSN, LoRA, Digital twin, Edge / Cloud computing, smart wearables, mobile AGVs, HPC, 5G, Wi-Fi 6, LoraWAN, Edge computing. | ||||
| Hardware Festo Didactic (Festo CP Lab, Festo Modular Production System), AGVs with industrial robots mounted (Mobile Industrial Robot MIR100, UR3, ABB Yumi, Festo Robotino, Milvus Robotics SEIT100), HTC Vive VR, Artec 3D Scanner, vertical farming demonstrator, Schneider Electric PLC, Raspberry Pi RevPi Kunbus, Nokia AirScale | Software IEC 61499 (Schneider Electric Ecostruxure, Eclipse 4DIAC), IEC 61131-3 (CodeSys), OPC UA (open62541, ProSys OPC UA, FactoryIO, Visual Components, Microsoft Azure Cloud. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
AIOTI DLT 3.xx
DLT Energy Efficiency |

Location: Belgium |
Cross-domain | Industrial implementations |
License: n.a.
Access: partner access feasible Contact: tom@viniblock.com |
proof of concept |
| Description: Despite tremendous improvements, Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT) continues to suffer a poor reputation when it comes to energy efficiency. This is mainly caused by the measurements taken around the Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism in the first landed protocols. Therefore, the AIOTI DLT working group agreed to set-up a series of DLT 2.xx Testbeds for the systematic evaluation of the footprint and energy efficiency of different protocols currently considered market ready. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: The DLT 2.xx test campaigns are executed following International Software Qualification Testing Board (ISTQB) standards and include a state of the art benchmark methodology that includes assessing the protocols both on business impact metrics (transactions-per-second, up-time, scalability) and DLT specific metrics. The integrity of the assessments is furthermore ensured by the timeline of installations being supported by the protocol suppliers and tests being executed by objective AIOTI DLT members in the presence of protocol representatives and objective observers. The outcome of the different test campaigns comes in the form of a factual report including the different DLT protocols and performance comparisons. | Technology: Hyperledger, Ethereum, IOTA, Ripple and Cardano | ||||
| Hardware On-Premise, Low-power devices, Edge & Cloud | Software DLT Toolbox combined with open source Software Testing tools and XBRL. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
AIOTI DLT 2.xx
DLT Protocol performance |

Location: Belgium |
Cross-domain | Industrial implementations |
License: n.a.
Access: partner access feasible Contact: tom@viniblock.com |
proof of concept |
| Description: Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT) has emerged with the promise to establish trust and enable new business models on autonomous systems. The exact implementation and performance of the many available DLT protocols still remains to be formally assessed. Therefore, the AIOTI DLT working group agreed to set-up a series of DLT 2.xx Testbeds for the systematic and objective evaluation of different protocols currently considered market ready. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: The DLT 2.xx test campaigns are executed following International Software Qualification Testing Board (ISTQB) standards and include a state of the art benchmark methodology that includes assessing the protocols both on business impact metrics (transactions-per-second, up-time, scalability) and DLT specific metrics. The integrity of the assessments is furthermore ensured by the timeline of installations being supported by the protocol suppliers and tests being executed by objective AIOTI DLT members in the presence of protocol representatives and objective observers. The outcome of the different test campaigns comes in the form of a factual report including the different DLT protocols and performance comparisons. | Technology: Hyperledger, Ethereum, IOTA, Ripple and Cardano | ||||
| Hardware On-Premise, Low-power devices, Edge & Cloud | Software DLT Toolbox combined with open source Software Testing tools. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
AIRQ DAO
AIRQ DAO Foundation vzw |
Location: Brussels, Belgium |
Smart cities, Climate action | Autonomous system – Air quality sensor network |
License: n.a.
Access: feasible Contact: tom@airqdao.foundation |
Testbed |
| Description: The AIOTI DLT 1.02 AIRQ DAO Testbed demonstrates the convergence of IoT and DLT into an autonomous system based on the AIOTI High Level Architecture (HLA) for data markets. Co-creation, micropayments and (smart contract) revenue-splits enable a ‘self-sustaining’ and financially autonomous IoT sensor network. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: The AIOTI HLA into practice. (“Co-creation & Revenue split”) Each air quality sensor integrates with the DLT network via a dedicated wallet. Local engaged citizens subscribe to notification services via micropayments. The sensor receives monthly payments, and an automated revenue split rewards the data aggregator, service providers and the AIRQ DAO foundation. If the sensor can earn its own value after two years, a smart contract orders his replacement. As such, only valuable sensors are maintained, and the network becomes (financially) self-sustainable. | Technology: Converged IoT & DLT, tokenization, micropayments, and smart contracting | ||||
| Hardware Solar cells, Air quality sensors, Cloud storage and virtualization | Software Ethereum vs. Cardano | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
CareCardio
CareCardio by Astea Solutions |

Location: Sofia, Bulgaria |
Health | Remote care, Medical self assessment, Digitalizing device readings where IoT is not available |
License:
Access: by demand Contact: Joro Penchev, jpenchev@asteasolutions.com |
deployed testbed |
| Description: CareCardio provides proprietary tech for best in class automated digitalization of medical devices paper printouts. It handles use cases of remote patient care where IoT-enabled devices are not available or the patient doesn't have control over how medical information is provided. It works with all sorts of lighting, phone camera and other user-centric means, with very high degree of fidelity and translates the picture to standard ECG and BP formats. CareCardio is published as a fully functional testbed, with the vision of a larger set of small-scale software solutions that follow a modular approach to solve technological problems and particular use cases in remote-care and point-of-care health-tech ecosystems and is open to all sorts of partnerships. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: The app provides digitalization of paper printouts or other photo images of cardiovascular medical devices readings (blood pressure, ECG, etc.) where IoT readings are not available. The data is being stored on a personal cloud account with tokenized permissions. It is currently being extended with other types of medical data readings, as well as a web dashboard that connects by API to any sort of clinician software. The primary concept of CareCardio and its parent suite of tools is to provide modular solutions to particular technology problems in larger partner solutions in the health-tech ecosystem. | Technology: Computer Vision, Medical Data Digitalization, Proprietary Algorithm | ||||
| Hardware handles readings from all commercial ECG (cardiovascular health) and blood pressure devices | Software Android, iOS | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
CERTH-HIT SMARTMLAB
CERTH-HIT Thessaloniki Smart Mobility Living Lab |

Location: Thessaloniki, Greece |
Smart Cities, Mobility | Real time traffic data in Thessaloniki (cars and trains); fleet management, etc. |
License: Microsoft 365, PowerBI, Visual Studio 2019 Enterprise, SQL Server 2017 Enterprise, Hyper-V Manager, Android Studio, Visum, SUMO, MATLAB and others depending on the activities
Access: feasible Contact: jose@certh.gr |
Testbeds |
| Description: Thessaloniki Smart Mobility Living Lab aggregates data from its local eco system in Thessaloniki via different types of sources. Through the fusion of the various datasets, new technologies, mobility services and prototype applications for passengers and vehicles are implemented. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Data collection and fusion, Data storage and processing, Data Analysis, models, and visualization simulation. Mobility services and prototype applications for passengers and freight vehicles | Technology: Transport simulation, Discrete Event simulation, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Digital Twin, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, Operational Research, Software & web development, Data basis, Object orientated programming languages (Python, .Net), MATLAB. | ||||
| Hardware n.a. | Software Smart sensors, Big data analytics tools, Modeling and simulation environments, transportation models algorithms, Open data platform (HIT Open Data portal). | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
FN LABS
Digital Catapult Future Networks Lab |
Location: United Kingdom |
Smart Cities, Health | n.a |
License:
Access: Contact: Maria Fonseca, maria.fonseca@digicatapult.org.uk |
|
| Description: Future Networks Lab brings together network, services, platform, and solutions providers in a technology-neutral space to experiment with IoT and 5G technologies. The network has enabled over 700 innovators to experiment with IoT technologies, leading to new products and services being brought to market in the UK and abroad. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Digital Catapult has partnered with Siemens, IBM, Arrow and Servicenow to support the UK’s dedicated facility for leading edge network technologies, the Future Networks Lab. Alongside some of this industry’s leading players, we are helping companies of all sizes access the latest networks technologies, development opportunities and advice for practical adoption, all to help de-risk innovation and show how these technologies can be rolled out in practice, not just in theory. | Technology: 5G, LoRaWan, Sigfox, NB-IoT, Nwave. | ||||
| Hardware 5G London node, UK 5G testbeds, including 5G Brighton. | Software 5G core, MEC, etc | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
DNET
Optimal Chicken Farm Management |

Location: Novi Sad, Serbia |
IoT, AI/ML, Poultry, Agriculture | Poultry production management, Animal wellbeing |
License: Annual SaaS license. Other arrangements for research purposes are possible.
Access: Remote Contact: srdjan.krco@dunavnet.eu, Srdjan Krčo; senka.gajinov@dunavnet.eu, Senka Gajinov |
Deployed testbed |
| Description: The objective of the testbed was to deploy and validate a platform for integrated poultry farm management with the focus on preserving the wellbeing of the chickens and establishment of a transparent agri-food supply chain. A set of IoT devices is installed on two poultry farms in Serbia to collect relevant data (environmental conditions, machine operational status, chicken behavior) that is processed using ML/AI based algorithms to generate advices and recommended actions to optimize the growing conditions, enable early stress detection and improve farm operations. The main benefits for the farmers stem from the comprehensive and continuous insights into the production process that lead to improving animal welfare, production optimization and better product quality. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: IoT, cloud, web, ML/AI | Technology: Computer vision, domain-focused data analytics | ||||
| Hardware IoT devices equipped with sensors for measuring air temperature, air humidity, CO2, NH3, air flow, light intensity, video cameras, microphones, edgeML gateway, LoRaWAN gateway | Software poultryNET – a cloud-based solution for data gathering and ML/AI based analysis that enables comprehensive activity management and monitoring. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
fortiss IIoT
fortiss Industrial IoT Lab |

Location: Munich, Germany |
Manufacturing, Energy, Smart Cities, Logistics, etc. | Simulations, IoT edge cloud infrastructure digital twins; Edge AI; PubSub communications for IIoT; Flexible mobile Edge-Cloud continuum across different domains, e.g., Manufacturing, Energy. |
License: open-source, Apache 2.0, Eclipse, GPLv2.0, GPLv3.0
Access: Yes, locally, and remotely Contact: Rute C. Sofia, sofia@fortiss.org |
Testbeds |
| Description: The IIoT Lab has as motivation to be an experimental and training interoperable and open playground for fortiss, and for partners (academia and industry). Focusing on multi-domain IIoT experimentation, the lab is organized into four main areas of experimentation and technological innovation, IIoT infrastructure simulations and digital twinning; Edge AI; advanced Pubsub communications for IIoT; flexible mobile Edge-Cloud continuum. Across each area, several open demonstrators are available to industrial and academic partners. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: Open, interoperable multi-domain experimentation lab for next generation IIoT applications and systems. OT-IT interoperability aspects; automated data matching between IoT sources and IoT services; industrial networks based on wired/TSN and Wi-Fi 6 (scheduling and time synchronization); dynamic container orchestration (based on ML); Information-centric networking applied to different domains. | Technology: Wi-Fi 6/Wi-Fi7; TSN/Ethernet; Web of Things/OWL/semantic technologies; IoT communication protocols and architectures, e.g., OPC UA, MQTT, AMQP, ICN; Kubernetes. | ||||
| Hardware IoT IP-enabled devices, e.g., sensors, Raspberry Pis with sensors, Beaglebones, etc.; Festo stations; Mobile robots such as Turtlebots; Wi-Fi 6 enabled APs (Intel NUC AX200/201; Xiaomi AR 3600, UP Core) and stations; TSN switches; end-user devices, e.g., smartphones, tablets, laptops; cameras. | Software Specific open-source software developed by fortiss for each use-case; TSN Linux; MQTT, DDS; Named data networking; Pytorch; Kubernetes/Docker. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
fortiss MLAB
fortissimo Mobility Lab |

Location: Munich, Germany |
Automotive, Aerospace, Health | Complex, safety-critical cyber-physical systems; Model-based systems engineering, incremental integration testing; fault-injection testing. |
License: LGPL v3.0 (Simulation)
Access: Yes (Simulated online; Physical on-site) Contact: Tiziano Murano munaro@fortiss.org |
Testbeds |
| Description: The fortissimo Mobility Lab demonstrates how model-based systems engineering (MbSE) concepts can be leveraged to design and implement safe, adaptive, and reliable software and system architectures within a flexible development process. The demonstrator platform includes physical rovers as well as their digital twins. The fortissimo Rovers are based on heavily modified scale 1 to 10 RC cars, equipped with a LIDAR, ultrasound sensors, and an RGB camera. The fortissimo Simulation closely replicates the dynamics and sensor properties of the physical rovers using the Gazebo simulation environment, while providing a standardized interface for their behavior specifications by means of the FMI standard. In both cases, the automotive use case includes advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving (AD) functions. The fortissimo Mobility Lab is unique in its ability to demonstrate the model-based engineering of safety critical cyber-physical systems – from its conception to its verification and validation. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: MBSE concepts for designing (e.g., the SPES methodology), developing (e.g., product line management), integrating (e.g., Co-Simulation), and testing (e.g., defect-based testing) complex cyber-physical systems. | Technology: AutoFOCUS3; co-Simulation by means of the Functional Mock-up Interface (FMI) | ||||
| Hardware Converted RC cars (scale 1:10); Raspberry Pis, Tinkerforge sensor and actuator platform (ultrasound, lidar, engine management unit), 3D-Printed hardware racks, RGB cameras, Microsoft Xbox Bluetooth controllers. | Software (Simulated) FMI, ROS, Gazebo, FMI adapter for ROS. (Physical) AutoFOCUS3, Ansible, Ubuntu, custom drivers, libraries, and glue code linking generated code to the target hardware. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
fortiss NMLAB
fortiss Neuromorphic Lab |

Location: Munich, Germany |
Manufacturing; Space; Health | Mobile Robotics, Space, Human Machine Interfaces, Machine Vision; Adaptive swimming robot control, Neurorobotics simulation. |
License: Apache
Access: Yes, locally, and remotely Contact: Axel von Arnim, vonarnim@fortiss.org |
Testbeds |
| Description: The Neuromorphic Lab showcases one use case of neuromorphic computing, namely in mobile robotics. In this use case, a Lamprey like robot is being controlled by a spiking neural network over neuromorphic hardware (the experimental Loihi chip from Intel). The robot is swimming in simulation, controlled by a network powering a series of coupled oscillators that move each joint in a coherent manner, over super low energy hardware. This demonstrator proves the potential of neuromorphic hardware in edge AI applications where energy efficiency is a key factor. Further use cases, like industrial robotic arms, low-latency event-based vision, in-car human machine interaction is investigated by the Neuromorphic Computing team. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: The Lamprey like robot controller has been trained with the Neural Engineering Framework (Nengo) to generate oscillations at its links that generates an efficient swimming movement. In the Lab, a recorded sequence of controller action is replayed live, enabling the user to visualize the robot while moving in real time, to navigate through the scene, observe the neural network activity. | Technology: Robotic simulation, neuromorphic hardware, central pattern generation, Hopf oscillators, Neural Engineering Framework | ||||
| Hardware Intel Loihi experimental neuromorphic chip | Software Neurorobotics Platform, Gazebo Simulator, ROS, Nengo | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
fortiss ROBLAB
fortiss Robotics Lab |

Location: Munich, Germany |
Manufacturing | Intuitive instruction of robot systems; Robot program synthesis from declarative goal specifications; Autonomous manufacturing execution systems; Automated anomaly detection. |
License: Depends on the case – contact for further information.
Access: true Contact: Alexander Perzylo, perzylo@fortiss.org |
Testbeds |
| Description: The fortiss Robotics lab is focused on research and innovation on robot-based automation solutions and collaboration with interested stakeholders. It aims at addressing real-world problems and transferring the latest academic achievements into industrially relevant demonstration platforms and use cases. The implemented showcases are used to evaluate, validate, and disseminate research results to a broad audience ranging from industrial partners and other academic institutions to interested students. They further act as an open platform for discussions and joint developments on applied research. The focus is on robotic systems engineering, in particular the intuitive instruction of robot work cells, the semantic interoperability of manufacturing resources for knowledge-based autonomous production, as well as model-based software development for robotics. Within the fortiss Robotics Lab, experiments are conducted that serve to validate theoretical research results. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Development of ontology-based semantic description languages for formal representation of automation knowledge, automatic reasoning components for interpreting semantic models, semantic digital twins of manufacturing resources, novel approaches to intuitive robot programming and work cell (re)configuration; autonomous manufacturing execution systems. | Technology: RDF, RDF-S, OWL, OWL reasoners, SPARQL, SHACL, ROS, OPC UA, UA node set information modeling, graph databases. | ||||
| Hardware Universal Robots UR5s, Kuka LBR iiwas, various vacuum and 2-finger parallel grippers, tool changers, automatic spindle system, F/T sensors, 2d/3d cameras, robot-mounted RGB projectors, 3D printers for rapid prototyping. | Software Neurorobotics Platform, Gazebo Simulator, ROS, Nengo | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
fortiss S-ENERGY
fortiss Smart Energy Lab |

Location: Munich, Germany |
Energy, Mobility | Energy Management Systems, Energy System Modelling, Energy System Simulation and Optimization |
License: Apache 2.0, GPLv3
Access: true Contact: Dr. Markus Duchon, duchon@fortiss.org |
Testbeds |
| Description: The fortiss Energy Lab, demonstrates research results and challenges related to current and future developments in the field of energy systems. The available demonstrators deal with various application cases and show how real problems can be addressed with findings from science and research and allow them to be presented to a wide audience in an easy-to-understand and vivid way The demonstrators are continuously developed and adapted to current problems. With our lab environment we address existing challenges in the context of research and industrial projects or in the form of student and scientific work. In the fortiss Energy Lab, we work on topics such as the modeling of software systems, into the physical aspects. Here, we investigate opportunities and methods for designing and modeling complex systems as a basis for optimization, monitoring and control, in which the modeling of physical context and prognosis techniques from the area ML/KI are applied. Another focus area deals with evaluating system behaviors and optimizing energy systems. By using our co-simulation environment, hardware in the loop experiments can be conducted and the interactions and control mechanisms of cooperating systems can be analyzed and evaluated. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Open, software-based monitoring and control of decentralized energy systems. Architectures, communication, and home automation protocols. Modelling and (co-)simulation of complex energy systems. | Technology: SESSIM, openEMS/iEMS, Matlab/Simulink, SGAM, SCADA, openAI gym, OPC-UA, EnOcean, Modbus, MQTT | ||||
| Hardware Enocean sensors and actuators, IPSwitch, Pac Sentron electricity meters, Smart electric thermal storage (PCM based), electricity storage (LiFEPO4), thin-layer photovoltaics, solar logger | Software fortiss software (service-oriented architecture for critical infrastructure monitoring, iEMS) or openEMS, Co-Simulation environment (SESSIM) | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
FhG IIS L.I.N.K
Fraunhofer IIS L.I.N.K. - Positioning - Identification - Navigation Communication |

Location: Nürnberg, Germany |
Industry/Logistic, manufacturing, Smart City, Health, automotive | Industry 4.0; intra-logistics; vehicle access systems, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS); sports tracking; validation |
License: Depends on the case – contact for further information.
Access: true Contact: Dr. Wolfgang Felber, wolfgang.felber@iis.fraunhofer.de; Nicolas Witt, nicolas.witt@iis.fraunhofer.de |
Testbeds |
| Description: In the “L.I.N.K. Test and Application Center” at its Nuremberg location, Fraunhofer IIS provides a realistic and application-oriented environment for developing, demonstrating, and evaluating pioneering technologies and applications in the fields of positioning, identification, navigation, and communication. It contains of various reference positioning systems including a 5G campus network to evaluate new communication and localization aspects of actual standardization discussion. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: Positioning for IIoT; indoor/outdoor/seamless positioning for logistic applications (including a truck drive through and loading ramps. | Technology: 5G campus network installation, large volume motion capture, precise motion reference systems, automatic measurement campaigns (robots). | ||||
| Hardware Interior space of almost 1400m2 (44m x 33m x 9m) and outdoor space of almost 10000 m2; whole volume 3D- positioning system (robot); 6DOF reference systems; iGPS (submillimeter accuracy), Qualisys (large volume MoCap, 30x20x6 m); Synchronized Reference IMUs, XSens, cometa Wave Track; Automated test setups for large scale, repeatable testing; 5G campus network; grandmaster clock. | Software PTP, NTP; Qualisys Track Manager 2021. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
HUAWEI EDGE
Huawei Edge Computing OPC UA over TSN Testbed |

Location: Munich and Berlin, Germany |
Manifacturing | TSN based OT and IT converged industrial automation networks; IEC 61499 and TSN for smart manufacturing; Edge-Cloud Synergy AI (Kubeedge, Atlas etc.) |
License: n.a
Access: true Contact: konglingbo@huawei.com |
Testbeds |
| Description: Converged OT and IT network through TSN technology, carrying heterogeneous traffics, such as automation control, optical inspection, and video surveillance, from the field to the edge. Both the need of Time-critical control traffic and bandwidth consuming traffic can be met. Edge AI for industry using IEF framework for deployment and IEC 61499 for industry component integration. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Heterogeneous traffics (Automation control, video, events) and industrial protocols (OPC UA, IEC 61499, Modbus-TCP) carried on the unified TSN network, where the delay and reliability requirements can be met by centralized auto-configuration. | Technology: TSN data plane using combined Priority/Time-aware scheduling and shaping; TSN control plane integrated with network calculus algorithms; brownfield device compatibility solutions; Edge AI integrated industrial automation control. | ||||
| Hardware TSN-IP switches (S67xx; S57xx); Edge computing gateway (AR502H); Any-to-ETH gateway prototype; Miniature automobile production line; Automated Optical Inspection and video surveillance cameras. | Software OPC UA supervisory control; IEC 61499 controller; TSN centralized controller; Network Calculus algorithm; Kubeedge; Mindspore (for AI) | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
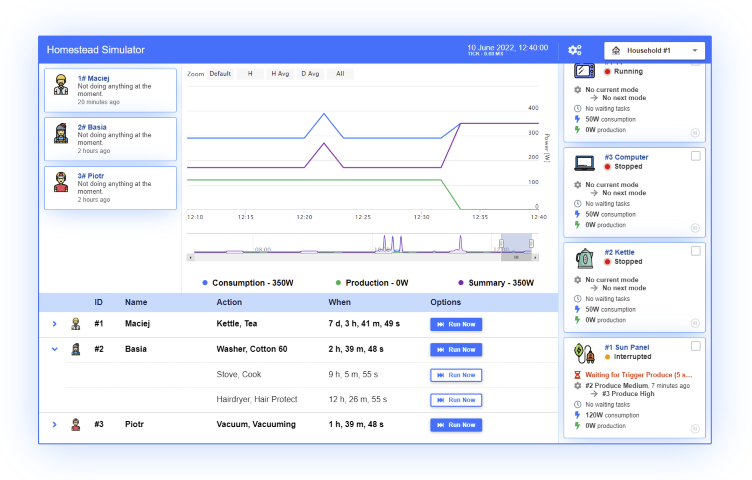
IHP HS
IHP Household Simulator |

Location: Frankfurt (Oder), Germany |
Smart Grid | Virtual environment for smart grid applications, testing demand/response algorithms, smart appliance control, renewable energy integration, energy efficiency evaluation |
License: N/A
Access: true Contact: Krzysztof Piotrowski, piotrowski@ihp-microelectronics.com |
use-case |
| Description: The household simulator allows to simulate the consumption and production patterns of electricity in virtual households by modelling virtual devices and residents. The resident schedule imitates daily routines. It can be used to test energy management algorithms through providing an environment for interaction between the algorithms and smart devices. The custom modelling language supports specifying metadata for households, residents, and devices, setting device usage schedules, and defining device characteristics. It also supports mathematical expressions, variables, and interaction points, allowing for detailed control over device behaviours. The schedule supports introducing variability and randomness in device usage. This approach enables simulation of real-world usage patterns. Provided API allows real-time changes to simulation parameters, fetching information on households and devices, triggering off-schedule tasks, and creating custom drivers. | |||||
|
|||||
| Concept: Testing energy management algorithms through interaction with virtual households imitating real-life usage. | Technology: Smart Grid, WebSocket, HTTP | ||||
| Hardware N/A | Software Java, Web technologies, Custom modelling language | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
IHP In-Lab
IHP In-Lab Demonstrator |

Location: Frankfurt (Oder), Germany |
Smart Grid | Environment for grid resilience testing, demand response, load balancing, energy efficiency and optimization algorithms, emergency scenarios |
License: N/A
Access: true Contact: Krzysztof Piotrowski, piotrowski@ihp-microelectronics.com |
use-case |
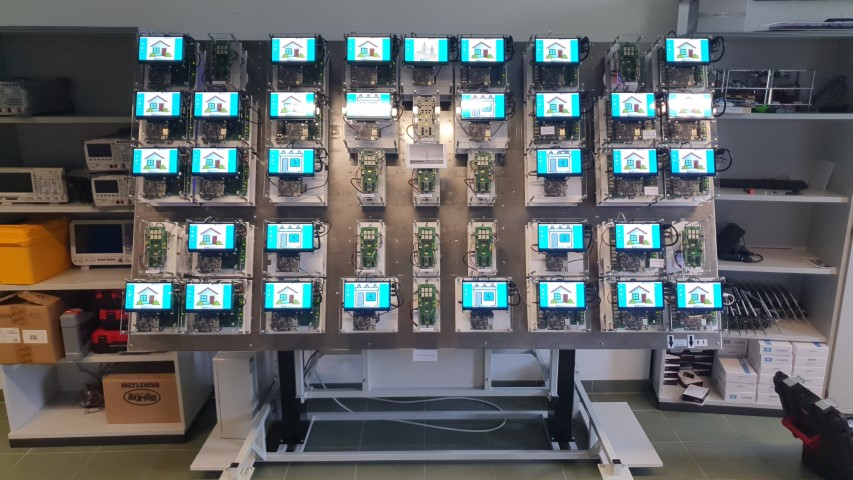
| Description: The in-lab demonstrator provides a controlled environment for simulating, testing, and evaluating energy management strategies and grid resilience algorithms, emulating a hierarchical energy infrastructure with primary and secondary substations, prosumer units, and transmission lines. It enables realistic load generation and measurement (lower voltages for operator safety). The emulator supports a range of customizable grid topologies, allowing project partners to replicate real-world scenarios, such as power outages and varying user behaviours, without risk. It is a cost-effective and safe way to advance grid resilience through repeatable and controlled experiments. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: Modular model of the smart grid, designed for evaluating energy management algorithms with the possibility to physically measure loads. | Technology: Smart Grid | ||||
| Hardware 33 blocks (BeaglePlay + custom boards) emulate 1 primary substation, 8 secondary substations, 24 prosumer blocks. Additional 12 blocks (custom boards) emulate transmission lines, which are controlled from the substation blocks. | Software Java, C, Custom middleware, Custom software | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
Citylab
Citylab Testbed |

Location: Antwerp, Belgium |
Smart Cities, Wireless Communication, IoT, Cross-domain | n/a. |
License: https://doc.lab.cityofthings.eu/wiki/Usage_Policy
Access: local and remote Contact: admin@lab.cityofthings.eu |
deployed testbed |
| Description: The UAntwerpen/IMEC Citylab testbed is a wireless testbed deployed outdoors in the city center of Antwerp. It is ideally suited for the experimentation with- and validation of- wireless technologies, protocols and solutions under real-life operating and interference conditions. Citylab supports a wide range of wireless technologies, including IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n, IEEE 802.15.4, Bluetooth Low Energy and LoRa(WAN) but ultimately it is up to the experimenters to decide what specific radio interfaces and technologies they want to use and what software/firmware to run on the nodes. Citylab contains 30 nodes that are deployed outdoors in the streets and on roof tops in a 0.5km by 0.5km area around the city campus of the University of Antwerp and 5 indoor nodes deployed at campus middelheim. | |||||
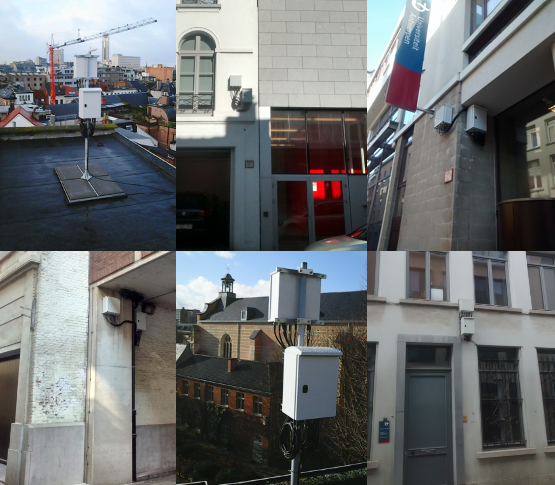

|
|||||
| Concept: In-vivo development and validation of wireless solutions under real-life city-scape operating and interference conditions. | Technology: IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac, IEEE 802.15.4, Dash7, LoRa(WAN), Bluetooth Low Energy, Edge Computing, ... | ||||
| Hardware Embedded PCs (PCEngines APU2), Ath9k, Ath10k, OpenUSBs, EFM32GG+RFM95W, EZR USBs | Software Linux, Openmote, Dash7, LoraMAC, ... | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
Homelab
imec Homelab |

Location: Ghent, Belgium |
Cross-domain | e-Health (incl assisted living), energy monitoring & optimization, indoor air quality monitoring, Validation of IoT technology for domestic use cases |
License: https://doc.ilabt.imec.be/ilabt/usagepolicy/index.html
Access: local and remote Contact: helpdesk@ilabt.imec.be |
deployed testbed |
| Description: The imec/UGent HomeLab is an actual standalone house offering a unique residential test environment for IoT services and smart living. A wide range of IoT technologies are deployed, and set-up flexibility to add new devices is offered by means of technical corridors, hollow floors and ceilings. The HomeLab team supports innovation at different stages from concept and co-creation with potential users, to early proof-of-concept testing in a real living environment. Supporting software tools and methods for integration, interoperability, data captation, sensor fusion are available. Application domains can be care, comfort, energy, mobility, media, safety, etc. Personalisation and contextualisation of future services for the realisation of the ‘intuitive home environment’ is a key research focus. As such the HomeLab offers a unique co-innovation space for industry, research groups, non-for-profits and other stakeholders involved in the realisation of future living concepts. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: key technological blocks supported | Technology: An open Home Automation system based on VelBus and OpenHab technology is installed, able to control all functional elements (screens, switches, doors, windows, etc) in the house. In view of sensors, actuators and user interfaces different off-the-shelf technologies and relevant standards (EnOcean, Grove, UPnP, ZWave, ZigBee, Hue…) are at hand. | ||||
| Hardware Many IoT devices( EnOcean, Grove, UPnP, ZWave, ZigBee, Hue), Softbank’s Nao and Pepper robot, prorietary air quality sensors (CO2), ... | Software OpenHab/Home Assistant, Data capturing platforms | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
IIoTLab
imec Industrial IoT lab |

Location: Ghent, Belgium |
Cross-domain | Industrial use cases including IoT technology and cobots/AGVs/conveyor belts |
License: https://doc.ilabt.imec.be/ilabt/usagepolicy/index.html
Access: local and remote Contact: helpdesk@ilabt.imec.be |
deployed testbed |
| Description: The Industrial IoT lab is an advanced test environment created to accelerate R&D in production and warehousing IoT technology. Located in Ghent, Belgium; the lab offers 300m2 of open experimentation space to foster regional and international co-operations in Industry 4.0 with a focus on smart and connected industries. Our research activities intersect robotics, machine learning, localization and wireless, and cloud computing. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: key technological blocks supported | Technology: 802.11a/g/n/ac, 802.15.4, Bluetooth, UWB, Edge / Cloud computing | ||||
| Hardware GPU servers, Embedded PCs (Intel NUC), Zolertia ReMote with UWB shield, Universal Robot UR-3 cobot arm, Franka Panda arm cobot,high-precision 1m diameter turntable, 2m linear conveyors, drones, AGVs, high precision IR positioning system | Software Ubuntu, ath9/10/11k, Contiki, Linux, custom drivers, libraries | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
Officelab
imec Officelab testbed |

Location: Ghent, Belgium |
Cross-domain | indoor localization & navigation, air quality monitoring, employee wellbeing, automated visitor guidance (robots/AGVs) |
License: https://doc.ilabt.imec.be/ilabt/usagepolicy/index.html
Access: local and remote Contact: helpdesk@ilabt.imec.be |
deployed testbed |
| Description: In the office location, several floors of the building are transformed into a real-life office lab. Wireless and wired sensor technology is deployed, and is open for research on tomorrow’s smart office applications for optimizing work spaces, visitor’s experiences, workers’ comfort, etc. The involved floors are equipped with 40 Intel NUC nodes, supporting several WiFi and sensor technologies. This offers an overall, mutlifloor testbed for distributed intelligence over 150+ nodes in real Office environment. Next to this the OfficeLab offers a unique real life experimental environment for development and testing of smart services based on IoT sensors and actuators. Specific interest of the IDLab research team goes to the use of social robots that are aware of the actual context and their environment based on continuous interaction with the surrounding IoT infrastructure. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: key technological blocks supported | Technology: 802.11a/g/n/ac, 802.15.4, Bluetooth, UWB, Edge / Cloud computing | ||||
| Hardware Embedded PCs (Intel NUC), Zolertia ReMote with UWB shield, various environment sensors (temperature, humidity, loudness, gas, CO2, ...) | Software Ubuntu, ath9/10/11k, Contiki, Linux, custom drivers, libraries | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
IMEC Smart Highway
imec Smart Highway Testbed |

Location: Antwerp, Belgium |
Smart Roads, Transport, Connected Mobility, 5G | 5G, V2X, Edge computing, Localization |
License: Depends on the case – contact for further information.
Access: local and remote Contact: johann.marquez-barja@imec.be, Johann Marquez-Barja |
deployed testbed |
| Description: The IMEC Smart Highway Testbed is a 5G-capable Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) testbed deployed at the E313 Highway in Antwerp. It contains 7 Road-side units (RSUs) mounted in the gantries over the highway as well as a number of vehicle-mounted Onboard Units (OBUs). Every RSU and OBU is equipped with radios for communication via the ITS-G5 and C-V2X V2X-standards. In addition they are each also equipped with a powerful local 'compute unit' and an SDR (USRP N310 in the RSUs, B210 in the OBUs). These not only enabled 5G-capabilities in the testbed but also enable experimentation with edge computing use cases and with new and upcoming communication standards. The testbed is also equipped with high-precision GNSS receivers (accurate to within 1cm, 5ns). These not only support the various V2X use cases but also serve as a useful baseline in the development of new localization technologies. | |||||
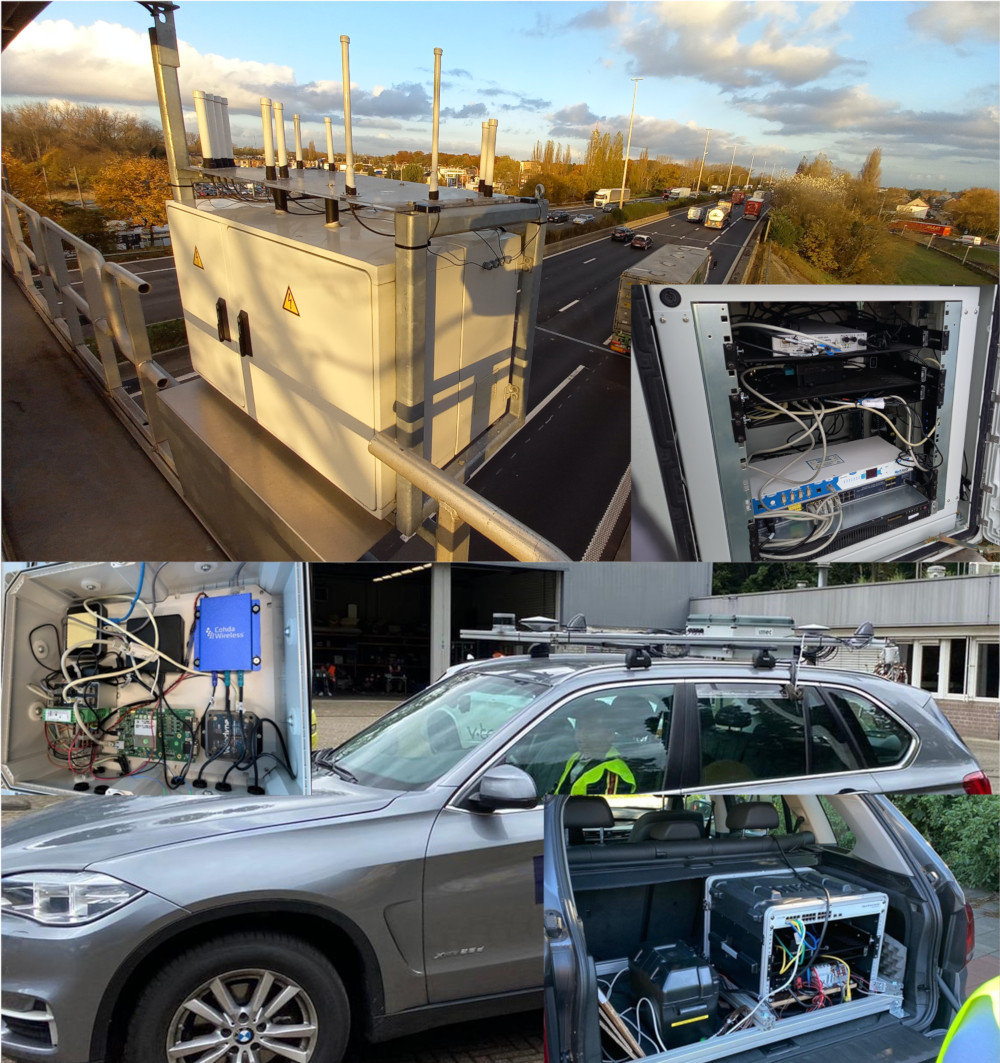

|
|||||
| Concept: In-vivo experimentation with- and development and validation of- current and new 5G, V2X, edge computing and localization technologies. | Technology: ITS-G5, C-V2X, Edge computing, 5G | ||||
| Hardware Supermicro servers, Intel NuC, USRP B210/N310, Cohda MK5, Cohda MK6c, Septentrio m2a GNSS receivers | Software Linux, Docker, K8S, LXC, OAI | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
IMEC w-iLab.t
imec w-iLab.t wireless testbed |

Location: Ghent, Belgium |
Cross-domain | use-cases supported |
License: https://doc.ilabt.imec.be/ilabt/usagepolicy/index.html
Access: local and remote Contact: helpdesk@ilabt.imec.be |
deployed testbed |
| Description: The w-iLab.t generic wireless testbeds consist out of embedded PCs in a pseudo shielded environment that are equipped with multiple wireless interfaces, including 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac, Bluetooth, IoT sensor nodes with 802.15.4 interfaces and user-defined and cognitive radios. It is up to the experimenters to determine which interfaces will be used, and what software/firmware is installed on the embedded PCs and/or sensor nodes.w-iLab.t 1 contains 44 nodes in a 30m x 10m datacenter. w-iLab.t 2 contains 100+ fixed nodes and 16 robots in a 60m x 20m room for high density and mobile experiments. | |||||
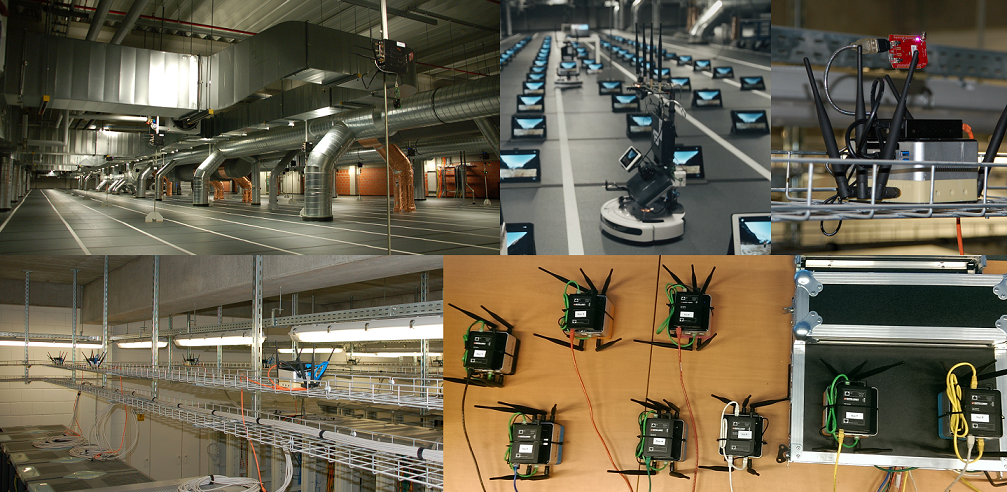

|
|||||
| Concept: key technological blocks supported | Technology: 802.11a/g/n/ac/ax (WiFi6), 5G, 802.15.4, UWB, mobile AGVs, Edge / Cloud computing | ||||
| Hardware Embedded PCs (Zotac, Intel NUC), SuperMicro server, USRP (x310, N210, B200, B210), Zolertia ReMote, 2xLTE femto cells (with EPC core), Android smartphones | Software Ubuntu, ath9/10/11k, Contiki, Linux, TSN, custom drivers, libraries, GNUradio, srsLTE | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
IN-DATA
IN-DATA |

Location: Barcelos, Vila Nova de Famalicão (Portugal) |
Energy | Load and renewable energy forecasting; energy sharing in local energy communities; energy efficiency; data-driven energy and non-energy services; battery storage optimization; smart electric vehicles charging; generative AI for data sharing. |
License: Proprietary
Access: Local or remote based on a specific agreement Contact: Ricardo Bessa, ricardo.j.bessa@inesctec.pt |
use-case |
| Description: Effective energy data management and sharing is crucial for advancing energy efficiency and fostering sustainable practices. Traditionally, data management platforms, notably for smart meters, have been advocated by Distribution System Operators (DSOs) and/or Transmission System Operators (TSOs). DSOs are progressively incorporating data on innovative services, extending beyond smart meter data to include customer data management and collaborative data sharing with TSOs. However, the prerequisite for explicit consent from consumers (data owners) to share their data with third-party service providers presents challenges, potentially disrupting various use cases and business models. This issue becomes particularly pronounced when dealing with behind-the-meter data, as barriers related to connectivity, data privacy, and security hinder seamless access. The challenges persist even when access to data is granted, engaging directly with end-users—consumers— is an ongoing challenge. This lack of direct engagement hampers essential activities like service design, co-creation, and the testing of AI-based solutions tailored to the specific needs and preferences of consumers. By addressing these limitations, the energy sector can unlock the full potential of AI for the benefit of both consumers and the broader energy community. To advance the development and validation of energy data sharing use cases in real-world settings, alongside the design of citizen-centric digital services and technologies at the local community level, INESC TEC partnered with Cooperativa Eléctrica do Vale d’Este, an energy cooperative acting as a local DSO and retailer. Together, they deployed a comprehensive range of monitoring equipment including total and individual energy meters, smart plugs, ambient temperature, and humidity sensors across dozens of households with PV, electric vehicles, heat pumps, electrical water heaters, among others. The unique feature of this initiative is the use of Data Space and semantic interoperability technology, particularly the open-source Data Space building blocks. In this community setting, these tools facilitate a wide array of energy and cross-sector services, fostering innovative consumer and community-centric business models. Furthermore, they ensure critical principles such as privacy, confidentiality, cybersecurity, sovereignty, and granting users full control over their data. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: The IN-DATA facilitates access to a local Energy Data Space, enabling AI-based energy service providers to collaborate and develop their solutions within a co-creation environment alongside consumers and prosumers. This space empowers users to collectively manage, share, and safeguard their personal data rights and usage in alignment with the EU Data Governance Act principles. Furthermore, it establishes an integrated data ecosystem, encompassing both real-time and historical data, while engaging citizens to drive the emergence of innovative data-centric services. These services aim to inspire shifts in consumer behavior, promote adopting new DER solutions, and foster business models that contribute to achieving net-zero objectives in the local energy system. This test bed is also a node of a Testing and Experimentation Facility (TEF) of the Horizon Europe project AI-EFFECT (“Artificial Intelligence Experimentation Facility For the Energy seCTor”, Grant Agreement no. 101069831). Potential use cases are 1) Test generative AI or differential privacy techniques for encouraging data sharing by creating synthetic datasets with minimal expert input. 2) Test peer-to-peer trading and energy-sharing mechanisms infused with AI technologies that can adapt and optimize strategies over time. 3) Test AI-based recommenders tailored to improve energy efficiency, e.g., enable contextually relevant and highly personalized recommendations to individual consumers or analyze energy consumption patterns at the household and community levels to identify opportunities for demand response and energy conservation initiatives. 4) State estimation, congestion, and voltage management in low voltage grids with a high penetration of distributed energy resources (e.g., photovoltaic, electric vehicles). 5) Control and optimization of behind-the-meter storage. However, other use cases can be proposed by start-ups, SMEs, or large companies interested in testing their AI-based solutions for prosumers, local energy communities, and low-voltage grids. | Technology: The IN-DATA architecture is designed for efficient data collection, processing, storage, and monitoring using various integrated technologies. Shelly Devices gathers environmental data, which is managed and processed by Python scripts. Once the data is collected, it is sent to RabbitMQ, a message broker that facilitates the exchange of data between different components of the system. The processed data is then stored in a non-relational database within the Sentinel bases. The architecture also includes DjangoFramework, MySQL, and Vue. DjangoFramework serves as an API layer, providing data to the front end, which is built with Vue. MySQL acts as a traditional database backend, storing structured data. Kubernetes orchestrates the deployment and scaling of these components. Cassandra within Sentinel handles specific data types, ensuring high scalability and resilience. Access to the data is managed through the dataspace, ensuring seamless integration and efficient data management. | ||||
| Hardware Forty homes are equipped with temperature, humidity, and energy meters with real-time communication. The homes have different assets, such as heat pumps (≥ 6), thermoelectric water heaters (≥5), electric vehicles (≥3), PV (at least five homes), and behind-the-meter battery storage (≥2). It comprises different typologies of residencies and citizens from different social backgrounds. Currently, there are 9 months of historical data of different temporal resolutions (e.g., with a minimum granularity of 1 min), namely active power consumption/generation, indoor temperature, and humidity. | Software A Data Space using the open-source components from the Horizon Europe ENERSHARE project (“European commoN EneRgy dataSpace framework enabling data sHaring-driven Across- and beyond-eneRgy sErvices”, Grant Agreement no. 101069831), namely the TSG Metadata broker, TSG Connector, Dynamic Attribute Provisioning Service, is operational. A dashboard for the consumers was developed for energy consumption visualization and analytics. The user interface uses Vue, Tailwind CSS, and TypeScript, creating a responsive and maintainable front end. Vue provides a dynamic, component-based framework for building interactive UI elements. Tailwind CSS offers utility-first styling, ensuring consistency and responsiveness across devices. TypeScript adds type safety and improves code quality by catching errors early. This combination ensures a robust, visually appealing, and efficient UI capable of handling real-time data visualization and user interaction seamlessly. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
X-Energy
X-Energy Lab |

Location: Porto, Portugal |
Energy, e-Mobility, IoT, IA | Electric power system studies based on digital twins. dynamic and transient studies, grid planning, grid resilience and black-start, protection and automation based on IEC61850 and AI-based digital substation concepts; Energy communities and EV charging management based on AI and edge-computing; Fault prediction and prevention in solar PV power plants; Demand side management and interoperability on household and industrial loads/appliances. |
License: Proprietary
Access: true Contact: Justino Rodrigues, Justino.m.rodrigues@inesctec.pt |
deployed testbed |
| Description: The X-Energy lab is an experimental test and validation facility focused on SmartGrids and Electric Vehicles integration. This facility hosts a set of capabilities enabling advanced studies combining physical and virtual assets. At its core, resides a physical low-voltage microgrid integrating renewable generation, energy storage, EV charging and miscellaneous domestic appliances, and a real-time digital simulation setup supporting Software-in-the-Loop (SIL), Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) and Power-Hardware-in-the-Loop (PHIL) capabilities. Among other applications, the existing assets support the development, test and experimental validation of innovative AI-based algorithms using digital-twins and IoT. The existing domestic appliances and in-the-house made prototypes and commercial solutions for EV chargers and distributed energy resources, allied to important advances in interoperability studies enables the exploitation of IoT concepts, can be used for this end. By other hand, the real-time digital simulation platform with SIL/HIL/PHIL capabilities enables the exploitation of the Digital-Twins concept to this end as well. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: The X-Energy lab – SmartGrids and Electric Vehicles laboratory – aims to provide an experimental testing environment for AI-based innovations, combining physical and virtually represented assets. The focus is the experimental test and validation of AI-based solutions applied to the energy sector. The existing real-time digital simulation platform with SIL/HIL/PHIL capabilities enables the development, experimental validation and use of Digital-Twins of the most varied physical assets, ranging from small, distributed energy resources to large power systems. Such Digital-Twins can be based in analytical and/or AI based elements. The support for SIL/HIL/PHIL would allow the interaction of the developed Digital-Twins with the physical world, namely the existing domestic appliances and IoT devices in general, in-the-house made prototypes and commercial solutions for EV chargers and distributed energy resources, loads, and more broadly, the low-voltage microgrid existing in our facilities. Among many possibilities, the proposed experimental environment aims to Validate AI-based solutions for - Energy sector addressing pressing needs such as EV charging management and control; management of distributed energy resources, Interoperability for IoT devices and intelligent distributed energy resources aiming demand-side response; operation of energy communities. - Digital-Twins, from intelligent distributed energy resources up to large power systems. - Grid studies dynamic and transient studies, grid planning, grid resilience and black-start - Preventive fault detection in PV power plants and other assets - Automation and grid protections, for distribution and transmission power grids. | Technology: • Digital Twins for distributed energy resources and energy power systems, based on analytical and/or AI methods. • Real-time digital simulation with SIL/HIL/PHIL capabilities, which would allow the interaction of the developed Digital-Twins with the physical world, namely the existing domestic appliances and IoT devices in general, in-the-house made prototypes and commercial solutions for EV chargers and distributed energy resources, loads, and more broadly, the low-voltage microgrid existing in our facilities. • Interoperability tools, enabling the integration of IoT devices with other physical assets and virtualized assets based in the real-time digital simulation platform. • Dataspaces, to enable a standardized way of accessing and managing data, while ensuring privacy, data sovereignty, and compliance. Data from various sources, including data resulting from the use of the experimental testing platform from X-Energy lab, can be combined, allowing participants to retain control over their data and manage access rights more flexibly. | ||||
| Hardware Low-voltage microgrid integrating renewable generation, energy storage, EV chargers and miscellaneous domestic appliances; Real-time digital simulator OPAL-RT, Power amplifiers EGSTON CSU100, Triphase PM15 and Doble F6350e; EV Simulator Trialog; dSPACE MicroLabBox II, miscellaneous domestic appliances with Wi-Fi connectivity; Multiple instrumentation such as energy analyzers, power analyzers, oscilloscopes, probes and sensors. | Software OPAL-RT software as RT-LAB, HYPERSYM, ePHASORSIM and eFPGASIM; MATLAB\Simulink®; DIgSILENT PowerFactory; PSS®E; PLECS®; Python, C++, C, among others | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
ITI DATAROOM
|

Location: Valencia, Spain |
Manufacturing | Multilevel energy monitoring; Horizontal and vertical data integration; big data analytics; 3D quality control; Digital twining; VR logistics laboratory; AR in warehouse management |
License: Free Access for demonstration. Pay per use for experimentation
Access: true Contact: innovacion@iti.es |
Testbeds |
| Description: DATAROOM is a Laboratory for demonstration and experimentation with Data for Industry 4.0, consisting of flexible manufacturing cells, robotics, automated warehouses, quality control. DATAROOM is the result of integrating all the results ITI is generating around industry 4.0 in one site. Its mission is to help companies to understand how to collect, manage and exploit Data in a production plant, and which tools and applications are available for it. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: Complete Data Cycle, Data Collection, Data Communication, Data Integration and Storage, Data Analysis, Data Simulation. Applications in predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, energy efficiency. | Technology: WSN, IIoT, OPC-UA, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Digital Twin, Big Data, Cloud Computing, Artificial Intelligence, Edge Computing, VR/AR. | ||||
| Hardware Modular production system (CP Factory); Robot Assembly Cell with Mitsubishi RV-4FL, Industrial Inspection cell (Zero Gravity 3D); AGV (Robotino); AR glasses | Software Festo MES, collaborative robot by MITSUBISHI, Radiatus by ITI https://radiatus.iti.es/, Data Hub by ITI https://datahub.iti.upv.es/, Deploids https://www.deploids.com/ by ITI; Zerogravity3D https://www.zerogravity3d.com/en/ by IT; IIoT protocols, e.g., Profinet, OPC UA, MQTT, etc; Kafka; multiple file formats, etc. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
LINKS DLT DH
Links DLT Digital Handshake |

Location: Turin, Italy |
Society | A decentralized solution for transparent and frictionless digital handshakes |
License: false
Access: true Contact: Alfredo.favenza@linksfoundation.com, Giacomo.corrias@linksfoundation.com |
proof of concept |
| Description: The AIOTI DLT 1.10 LINKS DIGITAL HANDSHAKE Testbed is set to demonstrate a blockchain platform aiming at helping gig economy workers to conduct business transactions with untrusted parties by leveraging smart contracts and dispute resolution mechanisms. The solution exploits the intrinsic benefits of DLTs to guarantee a verifiable process with automated payment and fair dispute resolution. The dispute resolution mechanism leverages a custom token and a decentralized escrow service to guarantee a fair and fast completion of the business transaction. The prototype is built on top of the EOSIO blockchain platform. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: A blockchain-based solution for making digital handshakes guaranteeing transparency on identity, code, and payments. Building a new form of trust in the digital handshake process (from platform to code) through an EOSIO blockchain-based solution. Fair and decentralized dispute resolution with a pseudo-random selection of jurors for reducing the cost-benefit ratio. Automatic token payments through a decentralized and bulletproof escrow service. | Technology: Smart contracts, tokenization, DLT-based dispute resolution. | ||||
| Hardware | Software Open Repositories https://github.com/Innovation-Advisory-Links-Foundation/DigitalHandshake-Backend https://github.com/Innovation-Advisory-Links-Foundation/DigitalHandshake-Frontend | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
LinksRE
Links DLT Reclothes |

Location: Turin, Italy |
Society | A decentralized solution for second-hand clothes recycles in the fashion industry |
License: false
Access: true Contact: alfredo.favenza@linksfoundation.com Giacomo.corrias@linksfoundation.com |
proof of concept |
| Description: RECLOTHES is a DLT testbed is set to demonstrate a blockchain-based solution (built on top of Hyperledger Besu) favoring the second-hand clothes recycles in the fashion industry. Reclothes allows a company operating in the fashion sector to implement a decentralized, transparent, and secure mechanism to record information relating to business relationships among partners and people interested in selling their second-hand clothes and/or buying second-hand upcycled clothes. To promote cooperation in the circular economy process, the solution implements a “double incentive” mechanism by adopting two different fungible token implementations. Leveraging private transaction processing tools, the consortium partners can define their commercial agreements and carry out transactions in confidence, without releasing any information unauthorized third parties. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: A decentralized solution for second-hand clothes recycles in the fashion industry. Designed as an enterprise blockchain-based network on Hyperledger Besu; allows confidential transactions visible only among business partners while keeping a transparent public history of quantities, processes, events, and payments; encourages individuals' participation in the circular economy through a double-incentive using two ERC20 token implementations, automating payments and rewarding mechanisms; provides a public interface for people who wants to support the eco-friendly fashion industry by sending second-hand clothes and/or buying upcycled clothes. | Technology: Smart Contracts, Tokenization | ||||
| Hardware | Software Open Repositories https://github.com/Innovation-Advisory-Links-Foundation/ReClothes-Backend https://github.com/Innovation-Advisory-Links-Foundation/ReClothes-Frontend | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
OULU 5G/6G
Oulu University 5G/6G Test Network |

Location: Oulu, Finland |
ICT; Energy; Manufacturing | Wireless connectivity and beyond for Smart Campus, Energy, Smart Living, Robotics, ITS and other verticals |
License: Varies depending on the components used and activities – contact for more information
Access: true Contact: ari.pouttu@oulu.fi liinamaa@oulu.fi |
Testbeds |
| Description: 5G/6G Test Network represents a campus-wide cellular network 6 . The network features the full portfolio of 5G terminals, higher frequency bands, cognitive management functionalities, system testing tools for new connectivity solutions and versatile vertical applications. The network evolution follows the research and standardization progress, acting as verification platform for theoretical 5G/6G research. The cellular network is complimented by an extensive mMTC/IoT connectivity network. | |||||
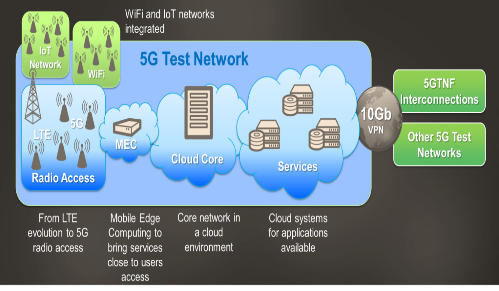
|
|||||
| Concept: The test network enables experiments for the next-generation wireless connectivity and its use for vertical applications. Its key components are wireless connectivity; AI/ML, processing, several vertical applications (energy, smart campus...). | Technology: 5G/6G and other radio access technologies (LPWAN (e.g., LoRaWAN), WPAN (e.g., BLE), WBAN (e.g., UWB), V2X). Edge computing, AI/ML, drones/robots | ||||
| Hardware 5 Macro and 20+ Pico base stations; 5G NR, LTE, NB-IoT and LTE-M; hundreds of Sim-cards; EPC and OpenEPC; 700 BLE beacon positioning; LoRaWAN network with 2000 sensors; ITS-G5/802.11p V2X OBU and RSU; 3 edge servers; rich set of measurement equipment | Software Frequency licenses; B1, B7, B28, B43 | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
POLIMI I4.0 LAB
Politecnico di Milano Industry 4.0 Lab |

Location: Milan, Italy |
Manufacturing | Production monitoring, programming, and optimization; Asset management and maintenance; Energy consumption optimization; Circular Economy ad disassembly operations; Collaborative and Autonomous Mobile Robots. |
License: Eclipse, Apache, OPC
Access: true Contact: Adalberto Polenghi adalberto.polenghi@polimi.it, Walter Quadrini walter.quadrini@polimi.it |
Testbed |
| Description: Industry 4.0 Lab is a tangible physical entity where the research activity in the innovative manufacturing management and planning approaches can be carried out in conjunction with a practical implementation in a “real-like” environment. Key components implemented include an assembly line based on the Industry4.0 paradigm and open architectures, including robotic stations, collaborative robots and Automated Guided Vehicles. Implemented scenarios encompass various research areas as production monitoring, programming and optimization, asset management and maintenance, energy consumption optimization, circular economy, dissemination, and robot/computer vision-assisted operations. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: AI and collaborative robotics supporting application development for advanced sustainable manufacturing. | Technology: AR; IIoT communication protocols; ML for MFG; collaborative robotics; distributed systems for manufacturing. | ||||
| Hardware Fully automated line with OPC UA-integrated PLCs for production and energy monitoring and control. Industrial Robot, Collaborative Robots, AGV, smart sensors, smartphones, tablets, laptops, wearable devices (HoloLens, Vuzix), 5G modems. | Software OPC UA; MQTT; Apache Kafka; MATLAB/Simulink, Python, MongoDB, k8s/Docker, Fiware. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
PSNC Labs
PSNC FutureLabs, PIONIER-LAB, Agriculture testbed |

Location: Poznan, Poland |
Smart Cities, Health, Agriculture | Smart Campus, Smart Spaces, Smart Parking, Smart Vending, Smart Farming |
License: n.a.
Access: true Contact: marcinp@man.poznan.pl |
Testbeds |
| Description: PSNC FutureLabs are the living labs in education, eHealth, smart City (https://futurelabs.psnc.pl/en/projekty/). Each of the labs provides different kinds of technologies, etc. PIONIER-LAB (https://pionier-lab.pionier.net.pl/laby/) - is one the largest Polish Research Infrastructure roadmap project, in which one of the laboratories is Smart Campus as Smart City. It creates the testbed of 12 smart campuses in Poland, with many sensors and infrastructure around smart spaces, parking, monitoring, energy, and others. The testbed will be available through the IoT/edge platforms for experimentation. eDWIN (https://www.edwin.gov.pl/) is a national platform for integrated plant protection, and provides access to network of agrometeo stations | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Access to data from distributed network of sensors, access to living lab building and spaces, access to data from network of agrometeo stations | Technology: IoT, Edge computing, HPC, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Big Data, Cloud Computing, AI, Edge Computing, Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality | ||||
| Hardware Sensor infrastructure; automatic air quality testing stations; Agrometeo stations; smart metering monitoring equipment; robotics platforms and arms; cameras. 42 camera motion capture kit, Grass valley rio kit, pablo neo panel, sony bvm-x300 OLED monitors, phabrix rx500 analyzer (rasterizer), 24-speaker ambisonic installation, scanners (e.g., Arri Scan) | Software Access to the PSNC computing infrastructure and DataCenter (PSNC is the major HPC and DataCenter in Poland) services and software stacks for AI/ML/DL, BigData, etc. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
solarlab
Solar Lab RES Cluster |

Location: Portugal |
Energy, Smart Buildings | Energy Production Optimization, Flexibility Management, Building Infrastructure Management |
License: n.a
Access: true Contact: n.samovich@enercoutim.eu |
Testbeds |
| Description: The Solar Lab is a Net Zero Energy Building (NZEB) that offers conditions to test energy systems, such as microgrid approach, IoT infrastructures, EV charging and other integrated components. Located in the municipality of Alcoutim, Algarve region - highest solar radiation in Europe. The Solar Lab is equipped with a PV installation, an EV charger, a weather station (high resolution sensors) DNI, UVE and other equipment, indoor sensors for IEQ monitoring, smart appliances for use as electric loads and Wi-Fi communication, electric energy storage unit. DEMO site was within H2020 projects SHAR-Q (smart energy) and VICINITY (IoT) and currently on BD4RNG (Big Data for Next Generation Energy) where concepts like interoperability between distributed energy systems and decentralized IoT infrastructure, were explored, tested, and demonstrated to the stakeholders. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Solar Demonstration Platform | Technology: Solar Lab; IoT platform, Smart Energy components, Smart EV Charging, IEQ sensors, technologies for system flexibility, testing of battery charging states, grid connection tests, local weather forecasting. Solar Demonstration Platform, Organizing 5G testbed, testing, integration. | ||||
| Hardware Solar Lab; PV system (11.7 kWp), batteries, EV charger Solar Demonstration Platform, CPV system (4 MWp), solar trackers | Software Solar Lab; Dynamic Building Audit, P2P energy trading platform. Solar Demonstration Platform, Smart Clean OM; Optimizing and improving management and prediction of DER; Energy sector digital twin. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
Synelixis IoT
Synelixis IoT Solutions |

Location: Athens, Greece |
Manifacturing, agriculture | Precision agriculture |
License: n.a
Access: true Contact: Theodore Zahariadis zahariad@synelixis.com Konstantina Fotiadou fotiadou@synelixis.com |
proof of concept |
| Description: SynField, is a Cloud based smart precision agriculture and smart/remote irrigation platform, aggregating weather, leaf and soil information in vineyards, orange, olives, coffee, and tea fields. Currently small networks of SynField are installed in more than 150 vineyards and 30 olive trees in Greece, Italy, Spain, Germany, Denmark, and Finland and in 10 coffee and tea plantations in south India. In details, SynField system targets small-medium sized farms, while it offers the following three main services. SynAir is a versatile sensor platform that accommodates a multitude of Air Quality sensors. The SynAir device, cannot operate by itself, and thus it should be connected to a SynField device, to read and forward the sensors’ data to the SynField portal. Currently, three basic SynAir versions are available, i.e., SynAir CO2, SynAir City, SynAir City+, supporting the detection of features such as temperature, relative humidity, CO2, Particulate Matter, VOC, NO2, CO, among others. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: Precision Agriculture & Sustainability, Supply Chain Intelligence, Cybersecurity & Risk Management, IoT & Connected Intelligence, Edge & Cloud Computing, Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning, SynField Platform Development | Technology: https://www.synelixis.com/internet-of-things/ | ||||
|
Hardware SynField, SynAir, SynOdos, SynRealy https://www.synelixis.com/ |
Software SynField | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
TEKNIKER SFHUB
Tekniker Smart Factory Hub |

Location: Gipuzkoa, Spain |
Manifacturing | Manufacturing, Tribology |
License: Contact Tekniker
Access: true Contact: Roberto González Velázquez, roberto.gonzalez@tekniker.es |
Testbeds |
| Description: Unified platform for the integration of services in a smart factory. The platform provides a single web interface to information acquired from testbeds, machine-tools, robots, special machines and tribometers. Depending on the asset, different types of information is provided (operational, process, condition, quality). | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: People counting, occupancy detection, crowd management, vehicle detection, sound analytics | Technology: Video analytics, mmWave technology, sound analytics | ||||
| Hardware Regular cameras, AI appliance, 3D cameras, mmWave sensors and sound detectors | Software Azure IoT HUB | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
Digital Nervous System
Ubiwhere's Digital Nervous System Testbed |

Location: Aveiro, Portugal |
Smart Cities, Mobility, Telecom, Smart Tourism, Blue Economy, ICT, Health, Energy, Industry, Construction | Awareness of VRUs in potentially dangerous situations, Intelligent and dynamic video caching, Object Detection in Video Streams (animals, people, cars, etc.), Collision risk warning, Monitoring dashboards for food production and smart parking scenarios, EV charging integration in street light poles, etc. |
License: IPR owned by Ubiwhere
Access: local and remote, based on assessment and agreement Contact: Ubiwhere DNS Testbed Team, dnstestbed@ubiwhere.com |
deployed testbed |
| Description: The DNS testbed operates like a real nervous system, in which the atoms are technological services that form the basis for testing and experimenting with innovative solutions for SMEs and start-ups. The DNS testbed offers 20+ reliable and user-friendly technological services to test innovative ideas and simulate real scenarios for different sectors to identify and solve problems quickly. | |||||
|
|||||
| Concept: The nervous system transmits signals to every part of the body to coordinate its actions. The Central Nervous System is a cloud solution for data integration and orchestration. The Peripheral Nervous System refers to edge computing solutions for IoT sensing and distributed processing of data | Technology: Cloud Computing, Edge Computing, IoT, AI (Computer Vision, Time-Series forecasting), EV Charging, Interoperability, Monitoring and Logging, UI and Dashboard | ||||
| Hardware 5G NR Small Cells (N78 3.5 GHz) - 5G SA; 4G Small Cells (B42 3.5 GHz, B7 2600 MHz, B3 1800 MHz) - 5G NSA; Edge nodes; IoT sensors; C-V2X equipment; user Equipments | Software Aggregation Platform for BI, API Billing Engine, API Gateway, Computer Vision for object detection, Container Registry, Data Visualisation Platform, Electric Vehicle Charging Platform, GitOps Platform, Identity and Access Manager, IoT Platform, Logging Platform, Monitoring Platform, OCPP Integration, REST API Keys and Auth | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
GAIA-5G
Universidad de Murcia Gaia-5G |
Location: Murcia, Spain |
Energy, Smart Cities | Smart Cities, Smart Campus |
License: n.a
Access: true Contact: ANTS research group, UMU |
Testbeds |
| Description: Gaia-5G is a testbed for 5G, computing and networking technologies, covering the whole campus in LoRaWAN, 802.11p and 5GNR coverage with our own network equipment. We also have distributed computation facilities linked via dedicated fiber links and a CWDM ring, with two open stack deployments, two hyperconvergence nodes, a Kubernetes environment and a PVE virtualization environment. The Gaia-5G Living campus is a deployment of IoT on the main university campuses with hundreds of sensors collecting data ranging from building / public transport occupancy, weather and air quality to photovoltaic production and wastewater processing parameters. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Practical demonstration of new communication technologies and computing paradigms over 5G, LoRa, etc. | Technology: 5GNR, LoRa, LoRaWAN, 802.11p, WiMAX; MEC | ||||
| Hardware RSU / OBU and low power ARM MEC embedded demonstrators | Software ETSI MEC, RADIO Mobile online, OpenFlow, PTP, etc. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
PP-IDM
Universidad de Murcia PP-IDM |
Location: Murcia, Spain |
Smart cities, Privacy-preserving Identity Management | Chain-enabled PP-IDM |
License: Open source (Apache 2.0)
Access: true Contact: skarmeta@um.es |
Testbeds |
| Description: The Chain-enabled PP-IDM Testbed is set to demonstrate the collaboration of distributed ledger technologies DLTs and privacy-preserving technologies (PETs) for achieving trustworthy environments where users are in control of their identity and can access services with guarantees of data minimization and not being tracked by services nor identity providers. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Users can obtain p-ABC credentials from a distributed infrastructure (OLYMPUS based) that secures critical points increasing the trust in all the scenarios. The IdM platform using smart contracts can unambiguously register existing identity providers and even keep track of service providers and their policies. Each service provider must communicate what information it consumes, and this is recorded in the DLT for later use. In this way, users can know in advance what data a registered service provider consumes and whether the policy it has finally demanded from them is the one it initially declared. | Technology: DLT, privacy-preserving Attribute Based Credentials (p-ABC), distributed identity management. Convergence between DLT and distributed IdM for trust increase. Smart Contracts | ||||
| Hardware Cloud storage, virtualization, smartphones | Software Hyperledger Fabric, OLYMPUS framework | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
UPM IoT Tactical Cloud
UPM Integration of IoT with Tactical Cloud |
Location: Madrid, Spain |
Smart Cities, Transport, Security and Defense | Disaster recovery, security, surveillance |
License: Varies depending on the components used and activities – contact for more information.
Access: true Contact: anamaria.bernardos@upm.es |
Testbeds |
| Description: Tactical Edge environments are those such as disaster scenarios or battlefields in which professionals (e.g., emergency first-responders, firemen or soldiers) usually have limited computing and communication resources, while having to deal with situations that evolve rapidly and unpredictably and high level of stress and need for risk control. The more and more, professionals are equipped with wearable IoT systems, both for self-control, situation assessment and information retrieval. There is a need for virtualizing resources and embedded them in specific tactical architectures that cannot be configured as a standard-cloud centralized service, but on edge and in a distributed manner. In this demonstration, hierarchical data processing for a defense use case, where the soldier wears a smart helmet connected to a tactical cloud architecture, that enables to receive data from external sensors (embedded in drone platforms, vehicles, etc.) in a communications environment that is continuously modified. A prototype of the installation is built for the European Defense Agency, but multiple applications for Law Enforcement Agencies and other partners are feasible. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Wearable IoT, Edge computing, resilient networks. | Technology: Data fusion, artificial vision, microservices architectures, IoT | ||||
| Hardware AR wearable helmet (HoloLens), routers, servers, ultra-wall (3x3 screens), wearable stress sensors, mobile devices. | Software MQTT, Kafka, Docker, MongoDB, Python, cloud services, OpenCV. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
UPM SMART CITIES
UPM Smart City spaces of the Future |
Location: Madrid, Spain |
Smart Spaces, Sustainability, Smart Healthcare, Tourism, Commerce. | Smart Cities, Smart Living Spaces, Connected Buildings, Flying IoT, Smart Transport, Security and Defense, Emergency Response. |
License: Varies depending on the components used and activities – contact for more information.
Access: true Contact: anamaria.bernardos@upm.es |
Testbeds |
| Description: The Experience Lab of the Spaces of the Future is a 160sq space for demonstration and service testing development located within CAIT Building at UPM Montegancedo Campus (Madrid, Spain). It is composed of reconfigurable semi-open rooms, specifically conceived to test personalized service concepts and interactive spaces. At the Lab, there are different technology enablers on top of which different service concepts have been trialed, for instance, IoT platforms on edge, multiuser indoor positioning systems based on hybrid sensors, a platform to provide multidevice collaborative augmented reality experiences, systems for multimodal natural (gesture-based, voice-based) interaction, concepts of smart objects (e.g., smart windows) and technologies for command-and-control centers. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: Edge platforms, indoor positioning, augmented reality, gesture-based, voice-based interaction, ultra-wall interaction, multisensor tracking, personalized services | Technology: IoT, artificial intelligence, microservices platforms behavior analysis algorithms, data fusion, | ||||
| Hardware High resolution ultra-wall, Arduino boards, smart cameras, interaction sensors (leap motion, Kinect, etc.), HoloLens, mobile devices, TV screens, Bluetooth beacons, ultrawideband beacons, servers, | Software MQTT, Kafka, Docker, MongoDB, Python, OpenCV, others. | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
UPM SMART DRONES
UPM Integration of IoT with Tactical Cloud |
Location: Madrid, Spain |
Security, Manufacturing, Logistics, Transports | Smart drones, UAVs, Security, Logistics |
License: Varies depending on the components used and activities – contact for more information.
Access: feasible Contact: anamaria.bernardos@upm.es |
Testbeds |
| Description: This testbed deployed in Montegancedo Campus is ready to demonstrate services deployed over fleet of drones (demos are carried out with >3 drones). The key asset is the software platform that controls the fleet service lifecycle, from mission configuration to real-time data visualization and sensor-based anomaly detection. Drones are governed as IoT sensing platforms, equipped with in-flight sensors, environmental sensors, and specific cameras (thermal cameras, LiDAR, etc.), mounted in depending on the use case. Different service scenarios have been deployed over the platform, e.g., infrastructure monitoring (e.g., for telecom towers), emergency response (for onsite fast evaluation of an emergency and first-aid kit delivery) and security applications (capacity control in bounded areas). Real-time artificial vision algorithms on-board and on the edge are used to monitor the service. Monitoring tools include specific applications for mobile devices, but also interactive solutions for command-and-control centers. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Drone fleet management & automation, real-time sensing. | Technology: Data fusion, artificial intelligence, artificial vision, optimization algorithms, tracking and navigation, adaptive interfaces. | ||||
| Hardware Drones, mobile devices, thermal cameras, LiDAR, ultra-wall. | Software MQTT, Kafka, Docker, MongoDB, Python, cloud services, OpenCV | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
VERSES
Verses DLT HSTP Spatial Web |

Location: Eindhoven, Netherlands |
Transversal | Convergence of IoT, DLT and AI |
License: Open source
Access: true Contact: info@verses.io |
proof of concept |
| Description: The VERSES Testbed is set to demonstrate the Hyper Spatial Modelling Language (HSML) and Hyperspace Transaction Protocol (HSTP) using COSM (Spatial Operating system) that enables interoperable, semantically compatible connections between connected software and hardware and includes specifications for 1) a spatial range query format and response language for requesting data about objects within a dimensional range (spatial, temperature, pressure, motion) and their content; 2) a semantic data ontology schema for describing objects, relations, and actions in a standardized way; 3) a verifiable credentialing and certification method for permissioned create, retrieve, update, and delete (CRUD) access to devices, locations, users, and data; and 4) a human and machine-readable contracting language that enables the expression and automated execution of legal, financial and physical activities. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Standard for Spatial Web Protocol, Architecture and Governance | Technology: COSM (Context-aware Spatial Operating System) Hyper Spatial Modelling Language (HSML), Hyperspace Transaction Protocol (HSTP) | ||||
| Hardware Autonomous drones, sensors, smart devices, and robots | Software Various software (services, platforms, applications, artificial intelligence systems) | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
VICOMTECH Digital Twin
Digital Twin for Remotely Operated Smart Manufacturing Line |

Location: Vicomtech, San Sebastian, Spain |
Manufacturing | Remotely Operated Smart Manufacturing Line, How to enhance the user-in-the-loop knowledge at a smart factory |
License: contact Vicomtech
Access: contact Vicomtech Contact: Dr. Ander Garcia agarcia@vicomtech.org |
deployed testbed |
| Description: In the testbed, a conveyor will move parts until they reach the working range of a Remote-Controlled Robot. A remote operator will handle the robot to pick the part and face it to a camera. Images from the camera will be transmitted by 5G technologies and the remote operator will decide if the part is valid in a full virtual immersive environment. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: Web order generator and ERP to monitor production; MES, controlling the production and orchestrating the actions of the other components (conveyor, robot, camera); conveyor, moving parts across the line and stopping when parts are detected at a predefined spot; digital Twin for remote quality inspection application, composed by a DT of the line and allowing the operator to control the robot and to inspect the parts; A Web quality inspection application, for use-cases not requiring the set of functionalities available with the DT application; Assest Administration Shell (AAS) based representation of the main components of the manufacturing line. | Technology: Digital Twin, 5G, ROS, Virtual Reality, Asset Administration Shell, OPC UA | ||||
| Hardware Manufacturing hardware, 5G Connectivity hardware, Oculus, UR Robot | Software Custom developments over Open Source software, ROS, OPC UA, Unity, PLC programming proprietary software | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
APICUS
Video Systems APICUS-PLT |

Location: Italy |
Manufacturing | Glass container Agile quality control, Non-ferrous casting components quality control, mechanical parts surface quality control |
License: n.a
Access: true Contact: Alessandro Liani, a.liani@videosystems.it |
Testbeds |
| Description: APICUS demonstrator platform includes physical anthropomorphic robot equipped with a set of machine vision systems dedicated to quality control tasks. The demonstrator uses machine vision technologies powered by deep-learning engine to quality control task of components manipulated by the robot. The pilot demonstrates integration of edge and cloud technologies that uses IIoT to share information for complex Agile manufacturing scenarios simulation. The station is connected to Cloud-based AI learning system based on Docker technology and NVidia GPUs accelerations. Different pilots are ready to test on various manufacturing sectors (Hollow Glass, high precision mechanical, foundry, furniture, field of household appliances, automotive. | |||||

|
|||||
| Concept: AI, Machine vision, Robotics, IIoT, Cloud computing. robotics, edge computing, embedded systems | Technology: Video Systems embedded machine vision systems, anthropomorphic robot, GPUs cluster | ||||
| Hardware Denso VS mod. 087G, On Robot grippers, NVidia GPUs cluster, Video Systems embedded vision devices, Video Systems stereo vision unit, photometric based surface quality control unit | Software Image processing modules, IngeniumPredicitveAIEngine | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
VIRTECH
Virtech Sofi aLab |
Location: Sofia, Bulgaria |
Smart Cities, Energy, Health | smart city, energy efficiency, smart buildings, active and healthy aging, e-health, sustainable development, e-mobility |
License: n.a
Access: true Contact: r.nikolov@virtech.bg |
Testbeds |
| Description: Experimental living lab facilities in smart energy, smart buildings, active and healthy aging, e-health, sustainable development, smart mobility (e.g., smart EV charging). | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: Big Data and AI enhanced smart services, GDPR compliant data exchange, interoperability. | Technology: Open-source platforms, e.g., FIWARE, openHAB, dataU | ||||
| Hardware Tablets, scanners, 3Dd Oculus Rift glasses | Software VR/AR edutainment, game design tools; 2D and 3D games | ||||
| Name | Provider | Domains | Use-cases | Access | Testbed stage |
|
BARTER
Vizlore Blockchain Assisted Real-time Transaction Execution and Repository Framework |

Location: Novi Sad, Serbia |
Smart city, smart building, e-mobility, agri-food, supply chain | Blockchain-Assisted Real-time Transaction Execution and Repository framework; Crypto-currency based micro-payments for IoT services in various domains’ machine to machine micro-payments integrated with IoT automation processes; Trust management processes in food supply chains; Food safety and quality tracking through complex food supply chains. |
License:
Access: feasible Contact: Milenko.tosic@vizlore.com sasha.pesic@vizlore.com |
Testbed |
| Description: The Blockchain-Assisted Real-time Transaction Execution and Repository framework (BARTER) Testbed is set to demonstrate a blockchain framework built on top of Hyperledger Fabric, Dash and VizLore's ChainRider service. It is a micro-payment enabler service that can be exploited to support a range of use-cases that need a secure and scalable M2M micro-payment solution, specifically designed for the IoT. Another part of the VizLore DLT Lab is the FT-CHAIN testbed. This testbed is built by Freie University of Berlin and VizLore Labs Foundation in a bilateral research project – set to demonstrate quality and safety tracking of food through complex food supply chains combining federated learning, DLT and IoT. | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Concept: BARTER is a decentralized private blockchain infrastructure with deployed smart contracts for automated micro-payments and data storage, allowing autonomous interaction between IoT ecosystem entities in carrying out everyday business workflows. Regulations, ethics, and business rules can be incorporated through smart contracts, which are stored on BARTER’s Hyperledger blockchain and provide REST API interface for integration with IoT devices in a secure manner. FT-Chain combines IoT system for food quality measurements (spectrometry methods), IOT system for environmental sensing, Hyperledger Fabric based ledger for trusted data sharing between parties and federated learning framework for high performance data analysis and decision making. The goal is to emulate complex processes and dependencies in food supply chains that might result in food quality degradation and contamination. | Technology: Converge IoT & DLT, micropayments, process automation, IoT platform with edge controllers, smart contracts | ||||
| Hardware VizLore IoT controllers – part of VizLore IoT platform – see https://smartaccess360.com/ | Software Hyperledger Fabric, ChainRider (chainrider.io), Dash, Bitcoin, H2020 PhasmaFOOD project SW platform. | ||||
Contribute to our Portfolio!
This page is an open-source project available on GitHub. Feel free to contribute!